CGPA vs Percentage: What is the Difference
Are you looking for the difference between CGPA and percentage?
Or, confused about how universities measure your academic performance?
Well, you are at the right place to know everything about CGPA vs Percentage.
Students in India and many other countries typically face the challenges of learning between two different grading systems: CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average) and Percentage.
Whether you are going to apply for higher studies, preparing for competitive exams, or job search, it is important to understand these measurement systems, so you can represent your academic performance accurately.
In this guide, we break down everything you need to know about CGPA and percentage, their differences, conversion methods, and when to use them.
Why do we use both Percentage and CGPA?
The Indian education system has used percentages for a very long time.
For years, educators have assessed student performance using the 0 to 100 scale.
Even though many universities and educational boards are adopting the CGPA system in recent years to comply with globally accepted standards, the percentage is still globally relevant as a criterion due to:
Historical Context: Within India, government jobs, competition tests, and the majority of traditional institutions still use percentages.
Comprehension Context: Parents and teachers are more accustomed to grading on a percentage.
Comparative Context: Percentage offers an intuitive scale that can be compared more easily in concept at a glance.
Standardization Context: Different institutions use different scales of CGPA (4.0, 7.0, and 10.0,) and percentage is the common denominator.
This dual context continues to create grounds in which students must also continually process and convert between the two formats, depending on what the institution or organization requires.
What Does Percentage Mean in Academic Grading?
Percentage in academic grading refers to your cumulative marks as a proportion of the total course marks represented on a scale of 0–100%.
It is a simple calculation:
Percentage = (Marks Obtained ÷ Total Marks) × 100
For example, if you scored 425 marks out of a total of 500 marks across five subjects:
Percentage = (425 ÷ 500) × 100 = 85%
This system has been a part of Indian education for many generations.
The primary reason for the popularity of percentiles is their simplicity; 85% clearly represents that you gained 85% of the total possible marks.
Despite the benefits of percentiles, they may vary slightly due to the difficulty of the exam or subject or across years, so it is not suitable in some instances to make absolute comparisons.
CGPA vs Percentage: Key Differences at a Glance
Understanding the basic differences in grading across both of these instruments can help you make easier decisions when engaging with academic requirements.
| Feature | CGPA | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cumulative weighted average of grade points across courses | Direct representation of marks as a proportion of total marks |
| Scale | Varies (4.0, 7.0, 10.0 depending on institution) | Universally on a scale of 0–100% |
| Calculation | Based on grade points assigned to letter grades | Direct calculation from raw marks |
| Precision | Typically reported to one or two decimal places | Usually represented as whole numbers or with one decimal place |
| Global Recognition | Widely used internationally | Less common internationally, more prevalent in India and some Asian countries |
| Volatility | Less affected by a single poor performance | Can be significantly impacted by outlier performances |
| Interpretation | Requires knowledge of the specific grading scale | Universally understood |
| Job Applications | Preferred by multinational companies and foreign universities | Universally, on a scale of 0–100% |
Why is converting CGPA to percentage important?
With CGPA usage becoming increasingly popular, there will still be many situations in which you will want to convert your CGPA into percentage:
- Government Exams: Many competitive exams and services, such as UPSC, SSC, etc., eligibility is given as a percentage.
- Job Applications: In India, many companies and online job sites require a percentage. — especially for entry-level jobs.
- Higher Education: Many universities have percentage-based cutoff criteria.
- Scholarships: Many scholarships specify eligibility criteria through a percentage threshold.
- Comparative purposes: When trying to compare CGPA with different institutions, especially when they use different scales.
In these situations, it may save time and provide certainty to use a CGPA to Percentage Calculator.
For conversions for more specialized activities, our CGPA to Percentage Calculator for UPSC has conversion methods relevant for these exams.
CGPA vs Percentage: Is CGPA Superior to Percentage? Pros and Cons Explained
Both systems are good and have their own limitations.
Knowing these will help you appreciate why both remain in our academic concerns.
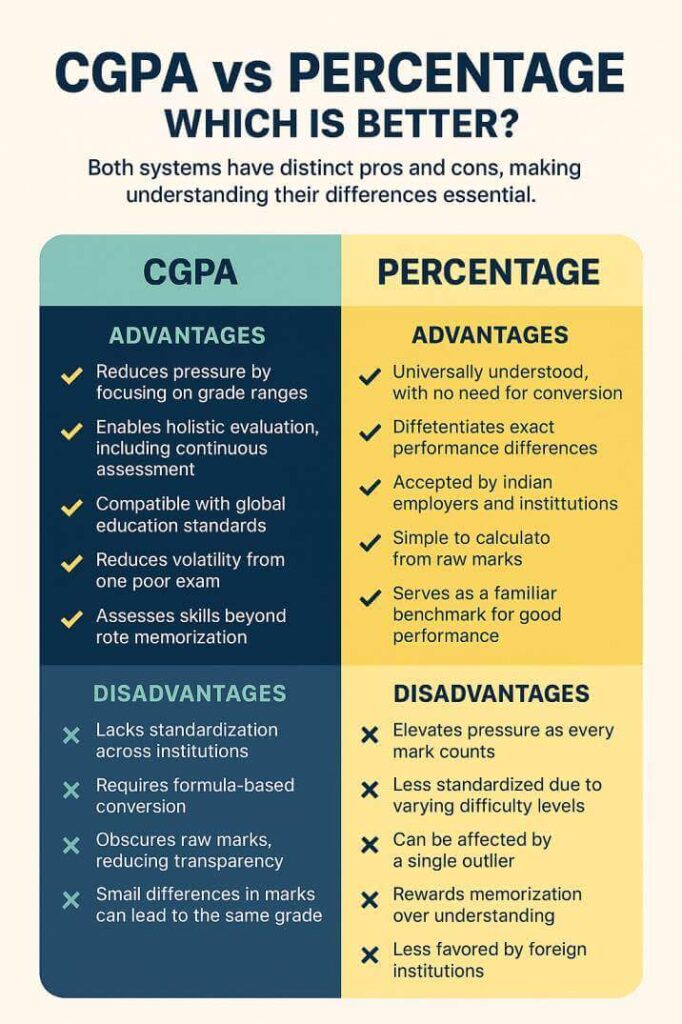
Advantages of CGPA
Reduced Stress: Measures degree ranges rather than specific marks
Holistic Assessment: Often includes RSMT assessments in addition to finals
International: Compatible with the Global Education Framework
Less Volatility: If an exam is bad, it will weigh less on the overall CGPA
Skill Assessment: Better illustrates overall competency and not rote memorization
Disadvantages of CGPA
Lack of Standardization: Various institutions have different scales across institutions
Complicated Process: For many purposes, conversion scales need to be created based on formulas
Lack of transparency: Raw marks can not be seen without digging
Threshold effect: fractions of marks may allow for the same letter grade at the boundary.
Advantages of Percentage
Universally understood: No need for conversion or explanation.
Precise differentiation: Shows exact performance differences.
Traditional acceptance: Widely recognized by Indian employers and institutions.
Direct calculation: Straightforward to compute from raw marks.
Familiar benchmark: Most people intuitively understand what constitutes good performance.
Disadvantages of Percentage
High pressure: Every mark counts, increasing exam stress.
Less standardized: Difficulty levels vary across exams and years.
Susceptible to outliers: One poor subject can significantly impact the overall percentage.
Emphasis on memory: Often rewards memorization over understanding.
Less internationally recognized: Many foreign institutions prefer GPA-based systems.
How Employers and Universities Interpret CGPA and Percentage?
As such, the way employers and universities view your academic history depends mostly on their context:
Indian Context
Traditional Indian companies generally ask for a percentage and have specified cutoffs (typically, 60% or 70% in the case of campus placements).
Government organizations only use percentages.
Indian universities often use percentages for admissions cutoffs (particularly for prestigious programs).
International Context
Multinationals are most often comfortable using CGPA since it is an international standard.
Most foreign universities ask for CGPA, and some will even convert it to their specific format (4.0 CGPA is a comfortable common standard).
International scholarships usually specify a GPA requirement.
Industry Differences
In technical fields like engineering, companies may look more to percentages for subject-specific grades than for their overall (aggregate) CGPA.
Industries like design or fashion might look less at specific grades and consider hard and soft skills within portfolio work.
When analyzing research positions, companies may look at more subject-specific performance than aggregate about academic performance.
This is meaningful because knowing these differences can allow you to try to present your academic performance in the best possible way for whoever is reviewing it.
When Should You Use a CGPA to Percentage Calculator?
An accurate conversion between grading systems can be crucial in several scenarios:
Job applications where the employer specifically requests a percentage
Higher education applications with percentage-based eligibility criteria
Scholarship applications that specify minimum percentage requirements
Competitive exam forms that require a percentage input
Creating standardized CVs when applying to multiple organizations with different preferences
Understanding your relative standing when compared with peers from different institutions
Our CGPA to Percentage Calculator simplifies this process by providing instant, accurate conversions based on your specific university or board’s formula.
Final Thoughts: Why Understanding Both Systems Matters
In the current globalized approach to education and employment, being fluent in both CGPA and percentage systems is crucial, not just useful.
If you are applying for a subsequent course of study, position, or clique of competitive exams, making the appropriate conversion from CGPA to percentage and percentage to CGPA ensures you maximize the academic profile you put forward.
The prevalence of both CGPA and percentage systems reflects a changing educational paradigm in India – accepting international standards and provision, whilst still preserving the traditional evaluative practices in assessment of learning.
As a student or employee, your dual fluency symbolizes adaptability and awareness of different educational frameworks.
In preparing for university, jobs, or internships, remember that your grade (CGPA or percentage) is one component of your overall academic and educational profile.
Practical knowledge, skills development, and extracurricular achievements also play crucial roles in your overall success.
If you want a quick conversion from CGPA to percentage and vice versa, try our comprehensive CGPA to Percentage Calculator.
Happy calculating!







